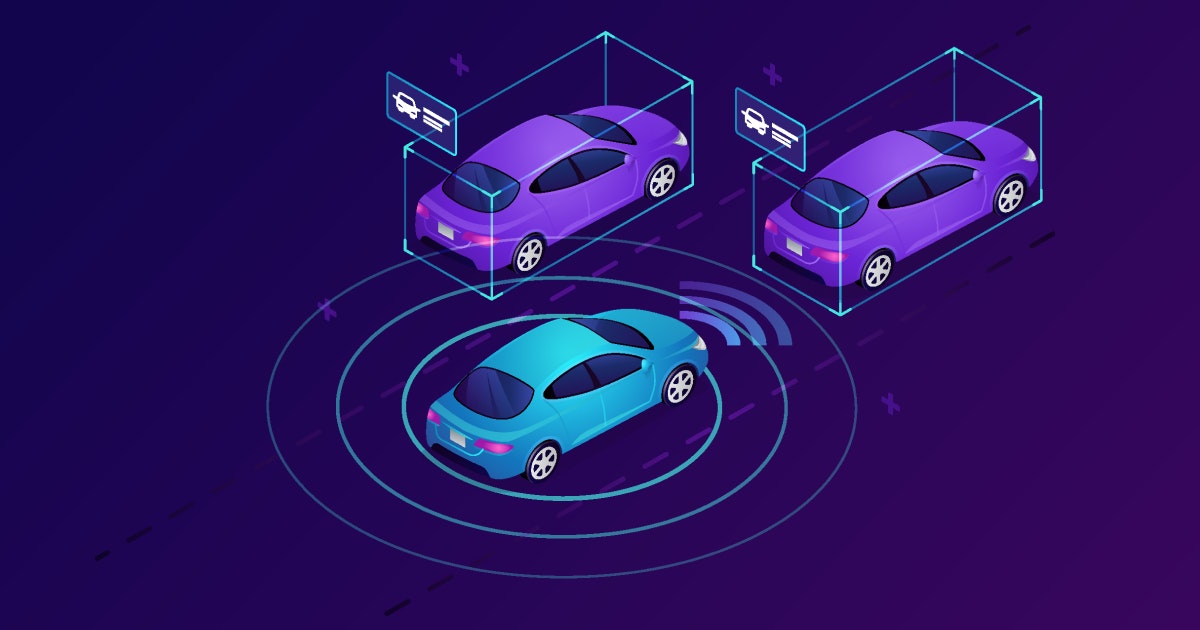
The Internet of Things or IoT is an ecosystem of connected devices that exchange data over a wired or wireless network. IoT is known to strengthen the foundation of a digital-first world by integrating cloud and edge computing to establish seamless connectivity.
Gartner predicts the penetration of over 15 billion Internet of Things devices into the enterprise infrastructure by 2029. So far, IoT has managed to carve a niche for itself in various sectors — be it manufacturing or health. The automotive industry is no exception either.
The state of IoT in automotive industry
Although the use of IoT in the automotive industry is still in its early phase, it is gaining momentum with each passing day with the rise in adoption of smart devices. Futuristic vehicles can communicate with each other thanks to internet connectivity, as well as the driver using IoT technology.
Next-generation vehicles cater to buyer needs with futuristic features like remote control via smartphones or customized seat adjustments on board. The performance of these vehicles is based on information collected in real-time.
IoT was introduced in its raw form in the automotive industry along with the advent of the Internet. Since 1994, computer diagnostics systems have been embedded into cars.
In 2000, USB and Bluetooth communication channels were added for more seamless integration between car systems. Entertainment or safety features were enhanced by implementing these. The influence of the Internet of Things over the automotive industry has grown over years.
Here are a few stats:
- It is estimated to grow up to $740 billion by 2025.
- Vehicle autonomy will reach escape velocity by 2023.
- By the same year, 70% of all vehicles will be connected to the internet.
The role of applications of IoT in the automotive industry
This industry is embracing new technologies that are going to revolutionize the usage and management of fleets. Implementing IoT-enabled smart devices and external sensors coupled with edge computing is disrupting the way the automotive industry operates.
Mobile devices enabled through AI-based applications and cloud computing keep you constantly connected with your vehicles. You can keep track of them, improve their performance, reduce downtime with predictive maintenance solutions, and achieve fuel efficiency.
Accelerate Your Auto Tech with Custom IoT Integration!
Explore SolutionsEight use cases of applications of IoT in the automotive industry
The IoT applications in the automotive industry have opened doors to limitless opportunities. They can help improve design, performance and reduce cost while ensuring quality control of the highest level.
Industry 4.0 has paved the way for the wider implementation of IoT by combining AI with networking technology. It allows cars to communicate wirelessly amongst themselves as well. The most common applications of IoT in the automotive sector are:
1. Fleet management
a. Real-time location monitoring of the fleet
IoT enables remote fleet management through three main technologies — RFID, GPS, and OBD-II. These sensors and onboard diagnostics systems fitted in vehicles provide real-time information about vehicle location. They collate data from accelerometers or gyroscopes to keep you informed about speed changes, idle times, and adherence to the route.
b. Weight or volume tracking of the vehicles
Measuring the exact weight of vehicles post-loading becomes challenging for logistics businesses. These innovative and advanced solutions utilize pressure sensors to calculate the actual weight in real-time.
Sensors are installed on the axle of a heavy vehicle, like a truck or trailer, to get real-time weight data. These replace digital scales and offer convenient weight measurement to eliminate unnecessary fines.
Similarly, they are deployed during the transport of liquids and other viscous materials, such as oils and chemicals. These Internet of Things sensors help in remote monitoring of tank levels, fluctuations in pressures, and raise alerts to prevent spillage.
c. Vehicle's performance statistics, like fuel and mileage
Research shows that 39% of the total operating cost of a truck fleet can be attributed to fuel. This makes it an important factor to consider in fleet management when calculating the operational costs of your supply chain business.
Fuel monitoring solutions use data from IoT-enabled sensors to allow users monitor fuel tank levels and usage. It also helps identify issues such as leaks or excessive idling in the automotive sector, so that you can maximize your efficiency.
Even poor driver behavior such as overspeeding and incessant breaking can adversely impact fuel efficiency and it can go down by 30-60%.
d. Tracking traffic conditions on the road
Connected vehicles deploy predictive maintenance alerts for receiving constant real-time data about traffic conditions, road closures, and public transportation travel schedules over the internet. Smart sensors on vehicles can communicate with nearby IoT-enabled devices and other vehicles.
IoT enables advanced transportation techniques such as self-driving or autonomous fleets and platooning. The proximity sensors and AI-driven systems predict any potential hazards or traffic delays, making self-driving safer.
The information such as satellite imagery for Google Street View, weather forecasts, and even social media posts reporting local incidents are communicated over wireless networks.
After processing through cognitive intelligence the crucial details are shared as notifications with drivers or autonomous driving systems, in real-time. IoT apps help monitor surrounding traffic patterns rather conveniently!
e. Route management to optimize mileage
IoT helps manage the route for a package from the pick-up point to the endpoint of its journey. Connected logistics companies can reap huge benefits by saving on fuel costs by taking the shortest possible route.
They can reduce shipment damages by avoiding poor roads and prevent delivery delays by avoiding congested routes. Route optimization software processes data from sensors and satellites to find the most cost-efficient road to minimize driving time and improve mileage.
f. Efficient time and driver management
IoT-based fleet management allows easy driver surveillance. Monitoring vehicle speed ensures safety on the road. It also reduces fuel usage and maintenance requirements drastically.
Fleet managers can keep track of the time taken for each delivery and even automate documentation procedures to reduce wait times for cross-border consignments.
In the case of high-speed driving, drowsy driving, and harsh braking, managers are alerted to avoid accidents. Such information gathered through advanced telematics solutions can be used to improve driver training programs.
2. Vehicle tracking
Fleet operators and owners use IoT to get a holistic view of their inventory. They can track the location of their vehicles as they move freight from one destination to the other. Real-time information sharing allows them to foresee changes in weather conditions or traffic congestion.
It helps in route optimization to ensure just-in-time delivery. Supported by GPS-enabled trackers, these internet connected services can communicate with their drivers about changes in route and delivery timeline.
Geofencing ensures each vehicle travels only within pre-set geographic boundaries to prevent any route violations.
3. Connected cars
Vehicles that stay connected to the internet and other IoT devices inside or around them are referred to as connected cars and one common use case of IoT is that it is used to track the vehicle's location.
a. Cellular vehicle to everything (C-V2X) technology
It is set to revolutionize the way automobiles interact with our world. It provides highly reliable and actionable information that can keep drivers safer on roads as well as improve autonomous driving capabilities. Being an integral part of a connected mobility ecosystem, the technology is set to provide vehicles with 360-degree awareness of their surroundings. Transportation Logistics Management (TLM) is bound to improve with the deployment of C-V2X, as it makes predicting traffic patterns easier and provides greater safety.
b. Vehicle-to-Vehicle (V2V) communication
These systems enable car owners to share information about their surroundings with other car owners. The technology relies on the Dedicated Short Range Communications (DSRC) frequencies and will work wirelessly.
As a part of this mesh network, each car will become its own node by capturing signals from nearby vehicles and sync data seamlessly. Any change in vehicle-to-vehicle systems can be detected instantly across every device connected within the range, including traffic lights or road sensors.
c. Vehicle-to-Infrastructure (V2I) communication
This takes place over Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS). It will facilitate the bidirectional exchange of information between the vehicle and the road infrastructure. That is what an IoT app development company can help you with.
Vehicle-generated data will be gathered and transferred wirelessly among sensors installed on the road infrastructure i.e. cameras, traffic lights, streetlights, road signs, lane markers, parking meters, and other infotainment systems.
The broadcasted data can be used to ensure driving within speed limits to avoid accidents and change routes based on modifications in weather conditions.
d. Vehicle-to-Pedestrians (V2P) communication
These systems detect pedestrian movements like people walking, children playing, wheelchairs, bicycles, and strollers. A vehicle-to-pedestrian smart sensor could be implemented to create awareness about the presence of people on the sidewalks.
In-vehicle infotainment systems that work on local networks powered by LiDAR technology can be used to raise collision warnings upon detecting pedestrians. Also, 360-degree cameras can be deployed to detect proximity and raise blind spot warnings.
Though these connections would require a new generation of IoT-based applications and mobile apps and in-vehicle infotainment systems, they support data streaming capabilities easily.
e. Vehicle-to-Networks (V2N)
Such infotainment systems use DSRC standards to interact with other vehicles as well as the road infrastructure. With this level of connectivity, vehicles will also be considered as a “device.” DSRC will help them in accessing data over the mobile network, LTE, and 5G infrastructure.
4. Automotive maintenance system
IoT automotive maintenance systems help fleet owners take necessary steps to prevent the sudden breakdown of their vehicles. The system alerts drivers about upcoming maintenance requirements and probable malfunctions in advance.
It helps avoid accidents and costly repairs while on their journey. Using predictive maintenance ensures you can be assured of the vehicle’s performance beforehand and reduce downtime.
IoT-enabled automobile diagnostics solutions provide fleet owners with precise information and help with adherence to delivery timelines.
5. Autonomous vehicles
The future of driving is predicted to be autonomous vehicles. It is still under development, though the implementation of IoT-infused semi-autonomous cars has already been done in the industry. These vehicles take on-spot decisions while partly controlling vehicle operations.
Drivers get support from these in vehicle infotainment systems in undertaking various activities such as parking or lane changing. The pace of developing autonomous vehicles for commercial use is accelerating as the technology will revolutionize how people commute and will also be beneficial for the environment.
6. In-vehicle infotainment and telematics
Telematics and IoT have revolutionized the automotive industry with in-car Wi-Fi capabilities. Telemetry refers to data transmission from a computer or device for remote monitoring, control, and so on, while IoT devices run on electric power and source data via sensors.
The 4G LTE connection enables automobiles equipped with these new technologies to enjoy functions such as video streaming, calling authorities in case of accidents, or even alert owner’s in case of theft. What a feat in connected car solutions.
7. Theft detection during the maintenance and manufacturing processes
The need to monitor the state of the equipment of automotive manufacturers has been realized in recent years. RFID tags are able to determine the parts that were stolen and the time of the incident. IoT implementation allows tracking of each part in real-time.
The manufacturing process in the automobile industry includes huge investment, therefore, keeping track of potential losses or thefts ensures the assets do not go missing and the process is not delayed. GPS monitoring systems having Google maps will help in tracking the person who committed theft.
8. Driver behavioral management
Such solutions monitor real-time driving behavior through the use of IoT-enabled sensors. The data gathered by IoT sensors can be used to detect and prevent accidents. Fleets are already being monitored for safety purposes with this technology.
With more than 90% of automotive accidents being caused by human error, it is important to target potentially dangerous driver behavior. It reduces accidents and cuts down repair costs.
Driver behavioral solutions use internet-connected devices that monitor everything from speedometer readings to accelerator movements. They track rash driving behaviors such as rapid acceleration and sudden braking.
The driving patterns are analyzed over time to provide training or warning to the drivers as and when required. Managers also receive alerts about driver fatigue, drowsiness, or other unsafe conditions to ensure safety behind the wheel.
IoT-Based Monitoring And Speed Control Of Automotive Motors!
Read NowThe future of IoT in the automotive industry
IoT is unlocking new value for all involved parties in the automobile industry and as it continues to evolve, it is steering towards a paradigm shift. By integrating new technologies such as AI and ML into IoT-backed networks, automobile manufacturers can develop better vehicle connectivity solutions.
The popular trends driving change are over-the-air software updates. These solutions will be capable of data analytics for preventive maintenance.
In addition to these innovations, the V2X connectivity is set to allow vehicles to drive themselves. These connected cars are capable of communicating through the deployment of vehicular electronics, embedded systems, and cloud connectivity.
Book a Free 45-minute Consultation with Our IoT Experts Today! Get a customized roadmap and strategies to leverage IoT for the automotive business.