Table of Content
If you are in the business of the Internet of Things (IoT), you must have come across the term "IoT gateway." You see - organizations commonly deploy a range of IoT devices. But with time, managing and monitoring these devices can become difficult.
Gateways offer the bridge between different communication technologies. You can say that a gateway is a medium that helps keep up a connection between the cloud and controllers, which are devices or sensors in the IoT ecosystem.
Gateways enable you to establish device-to-device or device-to-cloud communication easily and conveniently. Think of gateways as a specific software program or a hardware device.
IoT gateway: An in-depth analysis
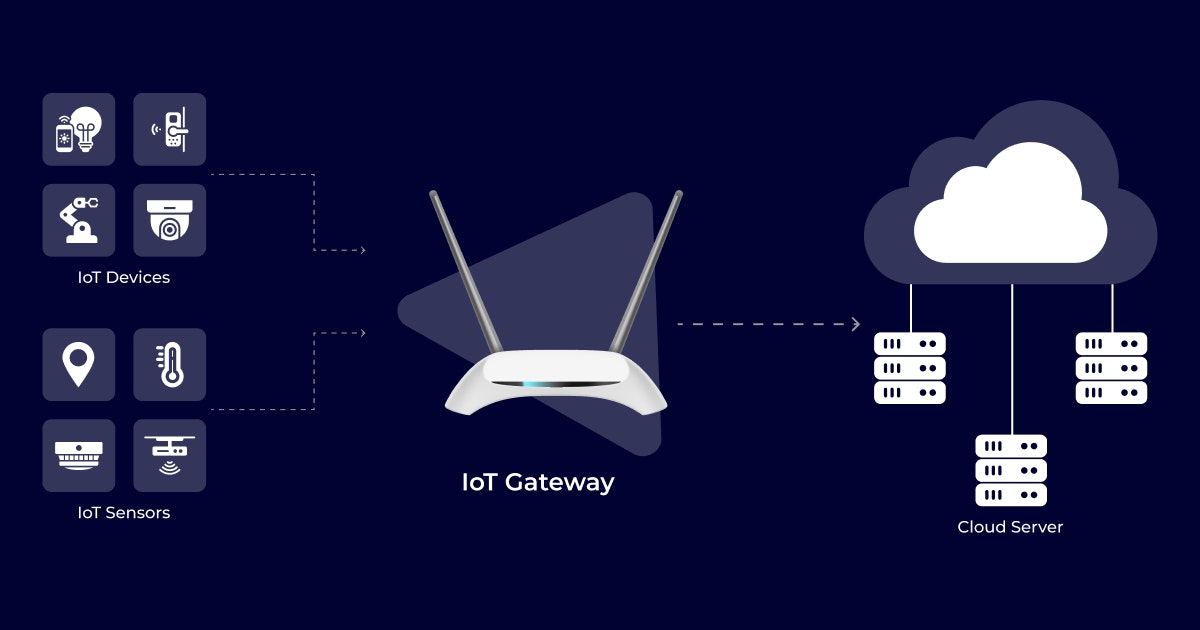
What is an IoT gateway, you ask?An IoT gateway can be defined as a smart computer that serves as a hub to control all the linked IoT devices, sensors, and actuators in a given environment.
A gateway functions as the entrance that gathers, processes, and filters data transmitted by various IoT devices before being sent to the cloud. It serves as the bridge between our physical and digital worlds.
Complex edge computing applications such as Artificial Intelligence (AI) run on more powerful IoT gateways, which process most of the data on Edge and allow real-time decision-making without help from the cloud.
How do IoT gateways work?
This one is a simple question - honestly! An IoT gateway carries out several crucial tasks, such as interpreting protocols and managing, filtering, processing, and encrypting data.
As mentioned before - a gateway that connects to the cloud lies between devices and sensors in an IoT ecosystem. A straightforward IoT gateway performs similar duties with the help of a WiFi router.
The common gateway utilizes the WiFi connection from an IoT system and then routes the data from the IoT device to the cloud. IoT gateways, however, are much more complicated. They help manage IoT device communications in the following ways:
- Device-to-cloud communications: The IoT gateway directs communication from several devices to the cloud infrastructure, acting as a single point of contact.
- Inter-device communications: The IoT gateway works as a central hub to allow IoT devices from different vendors to communicate amongst themselves.
- Data pre-processing: The IoT gateway filters and pre-processes data to save bandwidth by reducing the volume of data sent to the cloud.
- IoT device security: IoT gateways offer integrated security functionality and protect IoT devices from the threats of the public Internet.
- Smart edge: IoT gateways support fundamental device management by processing data from IoT devices.
Need a Tailored IoT Gateway Solution?
Contact UsIoT gateways are often more complex than WiFi routers because IoT devices use various protocols. As a result, an IoT gateway may need to support a variety of protocols to support all IoT devices in an organization.
The gateway must be able to route every form of IoT traffic to the right location in addition to supporting these IoT protocols. IoT gateways may need to cache data in the event of an internet outage locally or if the gateway is inundated with more data than it can process.
This is why they may be more complicated than WiFi or IoT routers. IoT gateways frequently offer failover clustering or the capacity to scale to handle growing workloads.
The architecture of IoT gateways
An IoT gateway is a central hub connecting IoT devices and sensors to cloud-based data processing and computing. Its architecture is simple yet unique. Here are 12 components that make up an IoT gateway:
1. Security
Security is one of the most critical factors in an IoT gateway architecture throughout the design phase. Using CryptoAuthentication™ chips, device security and identity are implemented in the gateway hardware.
Hardware tampering is done on the IoT gateway to boost overall device security. Additionally, a secure boot is used to prevent the gateway from functioning with illegal firmware.
To guarantee data integrity and sensor node confidentiality, all messages between the gateway and the cloud, as well as messages between the gateway sensor nodes, are encrypted. To maintain network security, data is encrypted as it travels to and from each node in an app.
2. Device layer
IoT sensors, protective circuits, networking modules, and a processor or microcontroller make up the hardware of an IoT infrastructure. The IoT gateway's operating system determines the type of hardware (processor/microcontroller), processing speed, and memory space. The design of the IoT hardware also heavily depends on the end-user application.
3. Data management
Data streaming, filtering, and storage are all parts of data management (in case of loss of IoT device connectivity with the cloud). Data from the sensor nodes to the gateway and from the gateway to the cloud are both managed by IoT gateways. Here, the difficulty is in reducing the time while maintaining data quality.
4. Operating system
The IoT application is a crucial factor in the operating system choice. Real-Time Operating Systems (RTOS) are employed when designing a gateway for simple to medium-sized applications. However, Linux is preferable when the gateway needs to do complicated activities.
5. Hardware abstraction
The abstraction layer enables independent hardware-free software development and management. This facilitates software evolution and upgrades by enhancing the flexibility and agility of the IoT application design.
6. Gateway data transfer
This component regulates how the IoT gateway connects to the Internet through Ethernet, WiFi, a 5G/4G/3G/GPRS modem, an IoT module, or any combination of those. Additionally, to conserve processing power and data plan costs, the gateway analyses and determines which data must be transmitted to the cloud and which data must be cached for offline processing.
7. Communication protocols
IoT gateway protocols are chosen depending on the volume and frequency of data sent to the cloud. Although cellular modules (5G/4G/3G), Ethernet, and/or WiFi are typically required for gateway connections, the underlying communication protocol layer is the TCP/IP model.
8. Cloud connectivity manager
This component manages scenarios including reconnection, device status, heartbeat message, gateway device authentication with the cloud, and being in charge of flawless connectivity with the cloud.
9. Sensor and actuator drivers
Sensors and actuator drivers provide the IoT device's interface with sensors and modules. Depending on what the IoT application requires, specific stacks are merged.
10. Custom software applications
The IoT gateway application is specifically created to meet the organization's needs. To manage data between the sensor node and the IoT gateway and from the IoT gateway to the cloud in an effective, safe and timely manner, the gateway application interacts with the services and functions from all the other layers or modules.
11. Firmware Over-The-Air (OTA) updates
The key to maintaining IoT device integrity is to keep the firmware updated and enable security upgrades and fixes to protect against constantly changing threats.
To protect device memory, power, and network traffic specifically, this component ensures that the Firmware Over-The-Air (OTA) updates are managed securely and effectively.
12. Device management and configuration
IoT gateways must keep track of all the connected objects and sensors with which they interact. This component keeps tabs on and controls sensor ecosystem-wide configurations, settings, properties, and IoT-connected devices.
Does IoT Work Without The Internet?
Learn MoreIoT gateway security: The best ways to manage
As you know, an IoT gateway acts as a network router, routing data between the cloud and IoT devices. Naturally, there is scope for data breach or leakage, resulting in the loss of sensitive user information and company reputation. Both advantages and disadvantages for IoT security can be brought about by these devices, including:
1. Data minimization
IoT gateways are in charge of screening data generated by IoT devices before it is transmitted - over the Internet - to the cloud. This aids in reducing the quantity of data exchanged and the potential for network communications or cloud-based servers to leak critical data.
2. Edge-based security
IoT gateways can include built-in security features that stand in between IoT devices and the Internet. Because IoT helps eliminate the security gaps frequently present in IoT devices, this can assist in safeguarding an organization's IoT devices and the sensitive data they gather from cyber threats.
3. Decentralized infrastructure
The IoT gateway's modest data processing capabilities provide security advantages and disadvantages. Edge computing for distributed data processing helps increase resilience and data reduction. However, a distributed architecture may be more challenging to safeguard because perimeter-based defenses cannot shield it.
Functionalities of IoT gateways
Modern IoT gateways often allow bi-direction data flow between the IoT devices and the cloud. This allows uploading IoT sensor data for processing and sending commands from cloud-based apps to IoT devices. Adding to that thought, here is a list of functions that a flexible IoT gateway could carry out:
- System analysis
- Data aggregation
- Device configuration management
- M2M/device-to-device communications
- Caching, buffering, mixing streaming IoT data
- Networking capabilities and hosting live data
- Managing user access and network security features
- Pre-processing, cleanup, filtering, and optimization of data
- Facilitating connection with older or non-internet connected devices
- Using IoT gateway applications, data visualization, and simple data analytics
IoT gateways: The ultimate bridge between IoT devices and servers
A genuine IoT gateway includes communication technologies that link the backend platforms for data, devices, subscriber administration, and end devices (sensors, actuators, or more complicated devices) to the gateway.
An IoT gateway has a computing platform that enables pre-installed or user-defined programs to manage data, devices, security, communication, and other gateway-related functions for routing and computation on Edge. Gateways provide both short-term as well as long-term benefits, some of which are mentioned below:
1. Data filtration
Gateways enable IoT devices to communicate with one another, changing the way they do so by transforming data into valuable information. They operate on Edge, deliver the required filtered data to the cloud, and accelerate reaction and communication times.
There is no requirement for a service provider to process the data because it can be handled and comprehended by the IoT gateway.
2. Risk mitigation
Security threats increase with the increase in the number of IoT devices. Thank goodness, a layer between the internet and IoT devices is provided by an IoT gateway, thereby preventing security issues.
3. Improved connectivity
Gateways function as universal remote controls that let you manage various IoT devices from one central location. It helps the establishments save a ton of time and effort. Facility managers interact with IoT systems through gateway internet devices using cloud-enabled applications to receive or send data to them.
4. Easy communication among devices
There are numerous devices and sensors in an IoT ecosystem. There is currently no common language used between these devices. Information is transmitted amongst them through gateways. It makes the entire communication process simpler.
Top 10 IoT gateways
IoT gateways are becoming increasingly important as the number of connected devices continues to grow. You cannot simply ignore what they offer in an IoT landscape if you want uninterrupted and safe data transmission and communication. Here are the top 10 IoT gateways to know about:
1. ReliaGATE 20-25
The ReliaGate 20-25 is LTE-ready, high-performance, and cloud-certified IoT edge gateway. It is a part of Eurotech IoT gateways. This one is best suited for challenging industrial environments and lightly rugged IoT applications because it was created using the exclusive Everyware Software Framework or ESF.
Functions
- Excellent security
- Powerful remote access capabilities
- Amazing hardware diagnostics options
- A wide range of operating temperatures
- Interesting customization opportunities
- High-quality Bluetooth and WiFi connectivity
- Fast and smooth Everyware Cloud integration
2. Kontron KBox A-201
This KBox gateway functions best as a multi-featured industrial computing platform and has a fanless, battery-less, and soldered memory design. By the way, the design is dubbed "wartungsfrei." The gateway's cost-effectiveness is still another strength.
Functions
- 15G shock resistance
- A wide range of hardware interfaces
- Powerful Intel Quark X1011 built-in processor
- Compatible with extreme operating temperatures
- Multiple mounting (desktop mounting, cabinet mounting, and DIN RAIL)
3. Advantech WISE-3310
This wireless IoT mesh network gateway from Advantech achieves high-performance levels and scores highly on the dependability scale since the Intelligent Gateway concept powers them. A sophisticated industrial IoT platform, the WISE-3310 gateway has built-in capability for 200 wireless nodes.
Functions
- Power-saving mode
- Linux 3.10.17 embedded into the hardware
- IEEE 802.15.4e and the 6LoWPAN standards
- Processor: Freescale i.MX6 Dual Cortex 1 GHz
- Has the fanless underlying design for embedded IoT apps
4. Cisco 910 Industrial Router
One of the rapidly growing sub-sectors in IoT is the market for smart cities. The rugged designs of the Cisco 910 Industrial Router were mainly created to enable functioning high-end smart city IoT applications.
Functions
- Glitch-free fog computing
- On-board memory capability
- Excellent horsepower support
- Different RF bands supported
- Cutting-edge modular slot design
5. Adlink MXE-5400i gateways
The Adlink IoT gateways are powered by the fourth-generation Intel Core (i3, i5, i7) processor and have official certification from Microsoft Azure. The gateways in the MXE-5400i series outperform in terms of CPU performance - while limiting overall power consumption.
Functions
- Rugged design
- Vibration resistant
- Cable-free construction
- Access to the Wind River IDP and the robust QM87 chipset for high performance
- Intel vPro technology with Smart Embedded Management Agent (SEMA) by Adlink for greater security
Industrial IoT Gateways: How To Choose The Best Option
Learn More6. B-Scada ethernet gateway
Unlike the bulk of the IoT gateways mentioned in this list, the B-Scada ethernet gateway offers end-to-end, real-time, wireless sensing capabilities. It enables the wireless IoT sensors to communicate with the cloud server and access sensor data from anywhere, anytime, on any web device.
Functions
- Pre-configured plug-and-play functionality
- A single gateway that can accommodate up to 50 sensors
- Three distinct frequency ranges: 433 MHz, 868 MHz, and 915 MHz
- Enables remote access to the retrieval of sensor data from any place
7. AR550E Series IoT Gateway
The AR550E Series IoT Gateway is a powerful IoT router specifically engineered for outdoor operations, manufacturing, transportation, and power utilities.
Functions
- Offers discrete advantages
- Network integration and sharing via virtualization
- Ethernet control and advanced Smart Grid operations
- Helps in retaining functionality under challenging conditions, such as temperature and humidity extremes and electromagnetic disturbances
- Multimedia and video services in different indoor and outdoor locations, including 'connected cars'
8. Dell Edge Gateway 500 Series
Dell Edge Gateway 500 is an ideal IoT gateway that excels at providing affordable solutions. It is simple to mount on walls and DIN rail and can be used in business and industrial contexts.
Functions
- OS: Ubuntu Core 15.04
- Compatible with M.2 SATA
- DDR3L (2GB) memory space
- Processor: Intel Atom E3825
- 32GB solid state hard drive
- Operates even in extreme temperatures (compatible temperature range: -30℃ to 70℃)
9. HPE Edgeline Converged Edge Systems
Edgeline IoT gateways are now available in two different configurations from HP - the ten and the 20. This gateway is meant to work with the HP Moonshot architecture to boost overall performance, density, and power levels.
Functions
- Superior data management
- Offers strict data security
- Utilizes a Core i5 processor from Intel
- Operates in sync with the Microsoft Azure IoT
- Faster gathering, assembling, and analysis of crucial data/figures
10. FlexaGate FG400 IoT analytics gateway
When web connectivity is poor and/or intermittent, and storage space or cloud bandwidth usage is an issue, the FlexaGate FG400 IoT analytics gateway is especially helpful.
Functions
- High performance
- Distributed memory architecture
- Handy 'passive cooling' features
- Minimizes processing, memory, and bandwidth costs
- Analyzing speed bolstered by the top-notch Ethernet input (RJ45 8×10 Gbps) and Ethernet output (RJ45 1×1 Gbps) capabilities
Enhance Your IoT Infrastructure with Expert Gateway Integration!
Explore SolutionsOver to you
As IoT technology evolves and the costs come down, the barriers to IoT adoption will also diminish. That means IoT gateways will also become stronger and more effective in what they do. If you are looking to get an IoT application built and want real experts to work on it.
Book a Free 45-minute Consultation with Our IoT Experts Today! Get a free customized roadmap and strategies to leverage IoT Infrastructure with expert gateway integration.